Are you concerned about your dog’s health and wondering about the abnormal BUN/Creatinine ratio? This informative blog post will help you understand what it is, its causes, and how to manage it effectively. Read on to learn more and ensure your furry friend’s well-being.
Your dog’s bloodwork can reveal a lot about their health, including the abnormal BUN/Creatinine ratio. It measures the balance between blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels, which can indicate kidney function and other health issues.
What is an Abnormal BUN/Creatinine Ratio in Dogs?
The BUN/Creatinine ratio in dogs is a measure of the ratio between blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels in the blood. BUN is a waste product of protein metabolism, while creatinine is a waste product of muscle metabolism. The normal range for the BUN/Creatinine ratio in dogs is 10:1 to 20:1. A BUN/Creatinine ratio that is higher than 20:1 is considered abnormal.

bun creatinine正常值 – Dqstdent – Source atevge.baoktte.com
Causes of an Abnormal BUN/Creatinine Ratio in Dogs
There are many potential causes of an abnormal BUN/Creatinine ratio in dogs, including:
- Kidney disease
- Dehydration
- Liver disease
- Protein-losing nephropathy
- Medications, such as corticosteroids
An abnormal BUN/Creatinine ratio in dogs can be a sign of a serious health problem, so it is important to consult with a veterinarian to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
BUN To Creatinine Ratio Understanding: Importance, Normal, 54% OFF – Source www.micoope.com.gt
Symptoms of an Abnormal BUN/Creatinine Ratio in Dogs
Dogs with an abnormal BUN/Creatinine ratio may show a variety of symptoms, including:
- Lethargy
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Polyuria (increased thirst)
- Polydipsia (increased urination)
If your dog is showing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a veterinarian to rule out an abnormal BUN/Creatinine ratio.
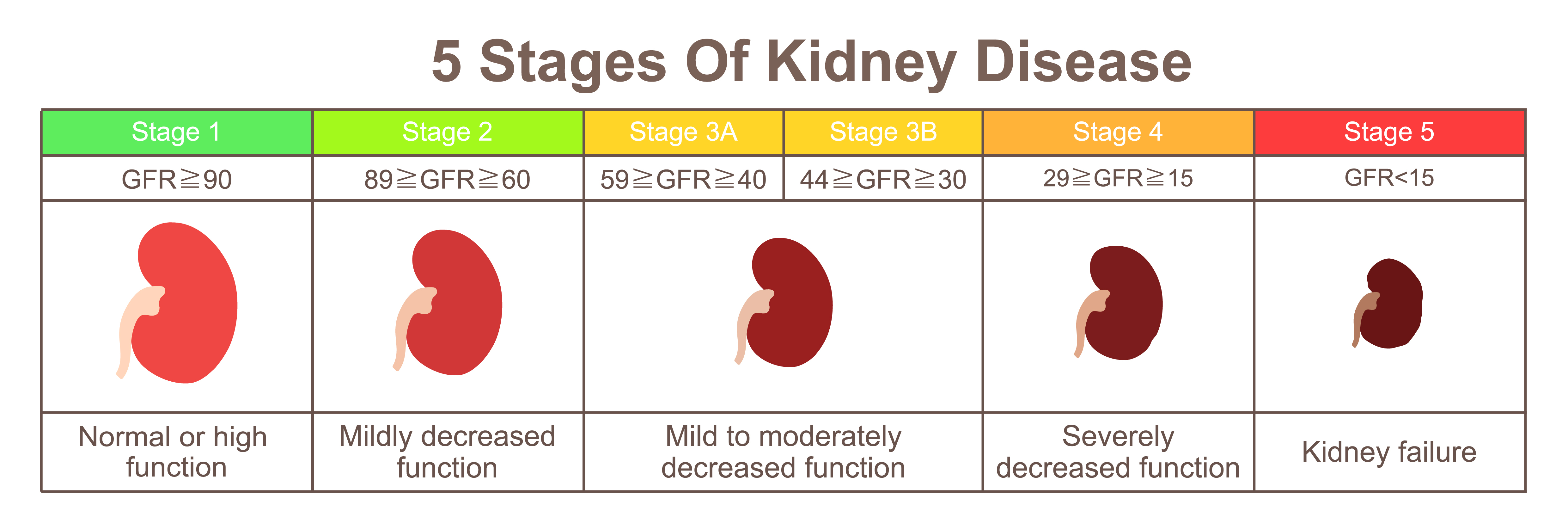
Creatinine Kidney Disease Chart – Source ar.inspiredpencil.com
Treatment for an Abnormal BUN/Creatinine Ratio in Dogs
The treatment for an abnormal BUN/Creatinine ratio in dogs will vary depending on the underlying cause. If the cause is kidney disease, the veterinarian may recommend a special diet, medication, or fluid therapy. If the cause is dehydration, the veterinarian will recommend increasing the dog’s water intake. If the cause is liver disease, the veterinarian may recommend a special diet or medication.

Cardiac Enzymes Fishbone Cheat Sheet Mnemonic Nursing Student This is a – Source www.pinterest.com
Preventing an Abnormal BUN/Creatinine Ratio in Dogs
There are some things you can do to help prevent an abnormal BUN/Creatinine ratio in your dog, including:
- Make sure your dog gets enough water.
- Feed your dog a healthy diet.
- Avoid giving your dog medications that can damage the kidneys.
- Take your dog to the veterinarian for regular checkups.
By following these tips, you can help keep your dog healthy and prevent an abnormal BUN/Creatinine ratio.
High Levels of Creatinine in your blood | HubPages – Source alphadogg16.hubpages.com
Tips for Managing an Abnormal BUN/Creatinine Ratio in Dogs
If your dog has an abnormal BUN/Creatinine ratio, there are some things you can do to help manage it, including:
- Follow the veterinarian’s instructions for treatment.
- Monitor your dog’s symptoms and report any changes to the veterinarian.
- Make sure your dog gets enough rest.
- Keep your dog’s stress levels low.
- Provide your dog with a healthy diet and plenty of water.
By following these tips, you can help your dog manage an abnormal BUN/Creatinine ratio and live a long, healthy life.
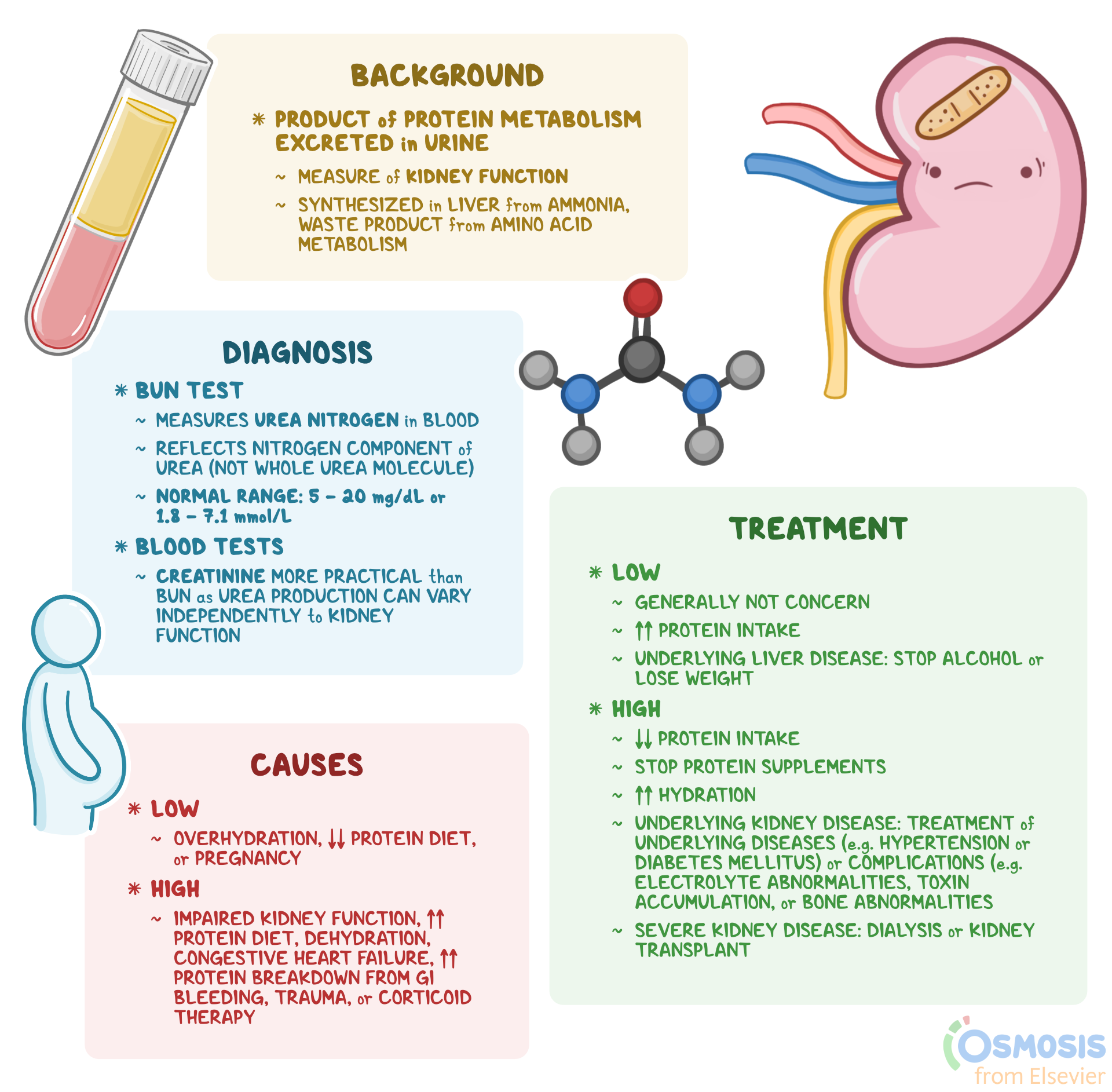
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN): What Is It, Causes, Treatment,, 50% OFF – Source www.gbu-presnenskij.ru
Conclusion of Abnormal BUN/Creatinine Ratio in Dogs
An abnormal BUN/Creatinine ratio in dogs can be a sign of a serious health problem, but it is manageable with proper treatment and care. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for an abnormal BUN/Creatinine ratio, you can help your dog live a long, healthy life.