Are you concerned about your dog’s kidney health? The Canine Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) to Creatinine Ratio is a crucial diagnostic tool that can help you assess your pet’s renal function.
Challenges of Monitoring Canine Renal Health
Monitoring canine renal health can be challenging due to the lack of early symptoms. By the time clinical signs become apparent, significant kidney damage may have already occurred.
Canine Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) to Creatinine Ratio: A Solution
The Canine Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) to Creatinine Ratio is a simple and cost-effective test that provides valuable insights into your dog’s kidney function. It compares the levels of BUN and creatinine in the blood, both waste products produced by the body’s metabolism.
A normal BUN to creatinine ratio in dogs ranges from 10:1 to 20:1. Higher ratios can indicate kidney dysfunction, while lower ratios may suggest dehydration or protein-losing nephropathy.
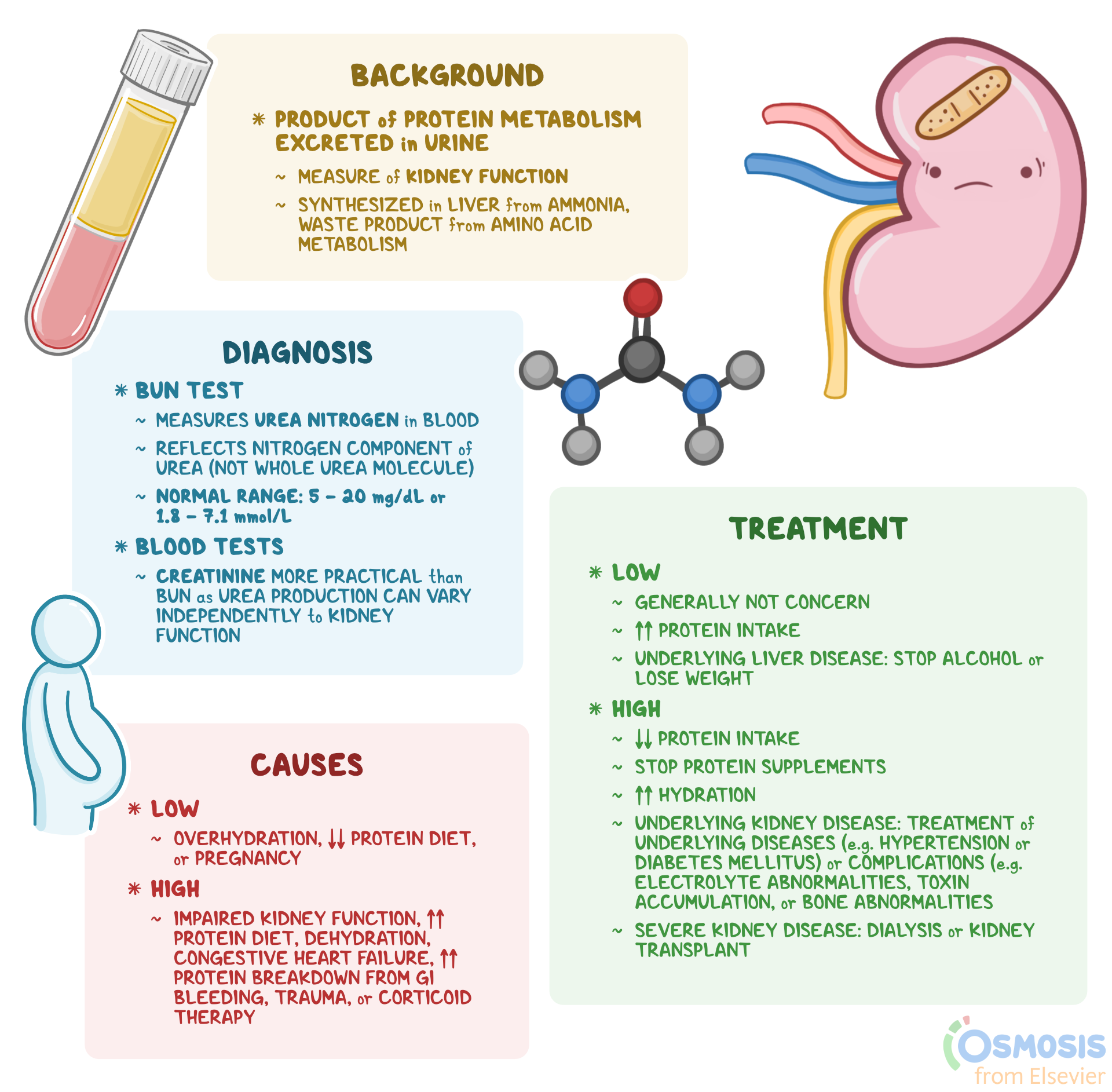
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN): What Is It, Causes, Treatment, and More – Source www.osmosis.org
BUN and Creatinine: The Breakdown
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) is a waste product of protein metabolism, while Creatinine is a waste product of muscle metabolism. Both are excreted through the kidneys, so changes in their levels can indicate kidney function.
History and Myths of Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio
The Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio has been used for decades to assess renal function. However, some misconceptions persist, such as the belief that a high BUN ratio always indicates kidney disease.
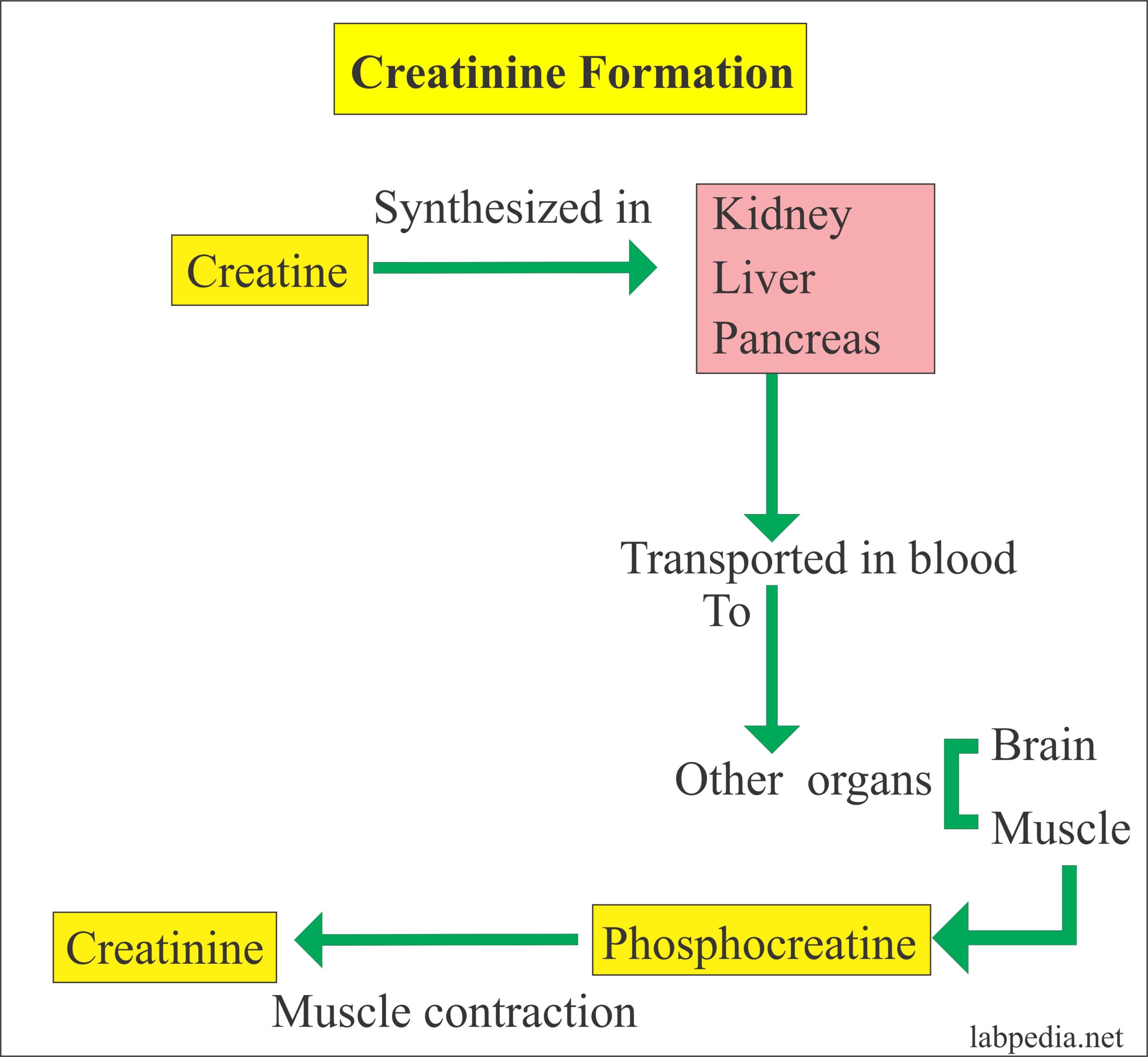
Creatinine clearance pcalc – noredmidnight – Source noredmidnight.weebly.com
Unveiling the Hidden Secrets of Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio
The Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio is not just a diagnostic tool. It can also provide insights into your dog’s overall health and hydration status. For example, a low ratio may point towards dehydration.
Recommendations for Interpreting Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio
Interpreting the Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio requires a veterinary assessment. Factors such as breed, age, diet, and hydration can influence the results. Your veterinarian will consider all these factors to provide an accurate diagnosis.

Pdf Diagnostic Evaluation Of Urea Nitrogencreatinine – vrogue.co – Source www.vrogue.co
The Role of Urine Specific Gravity in Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio
Urine Specific Gravity is another test that can complement the Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio. It measures the concentration of urine, which can indicate kidney function. A high urine specific gravity may suggest dehydration.
Tips for Optimal Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio
Maintaining a healthy Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio involves providing your dog with a balanced diet, adequate hydration, and regular veterinary check-ups. Limiting protein intake may be beneficial in managing kidney disease.
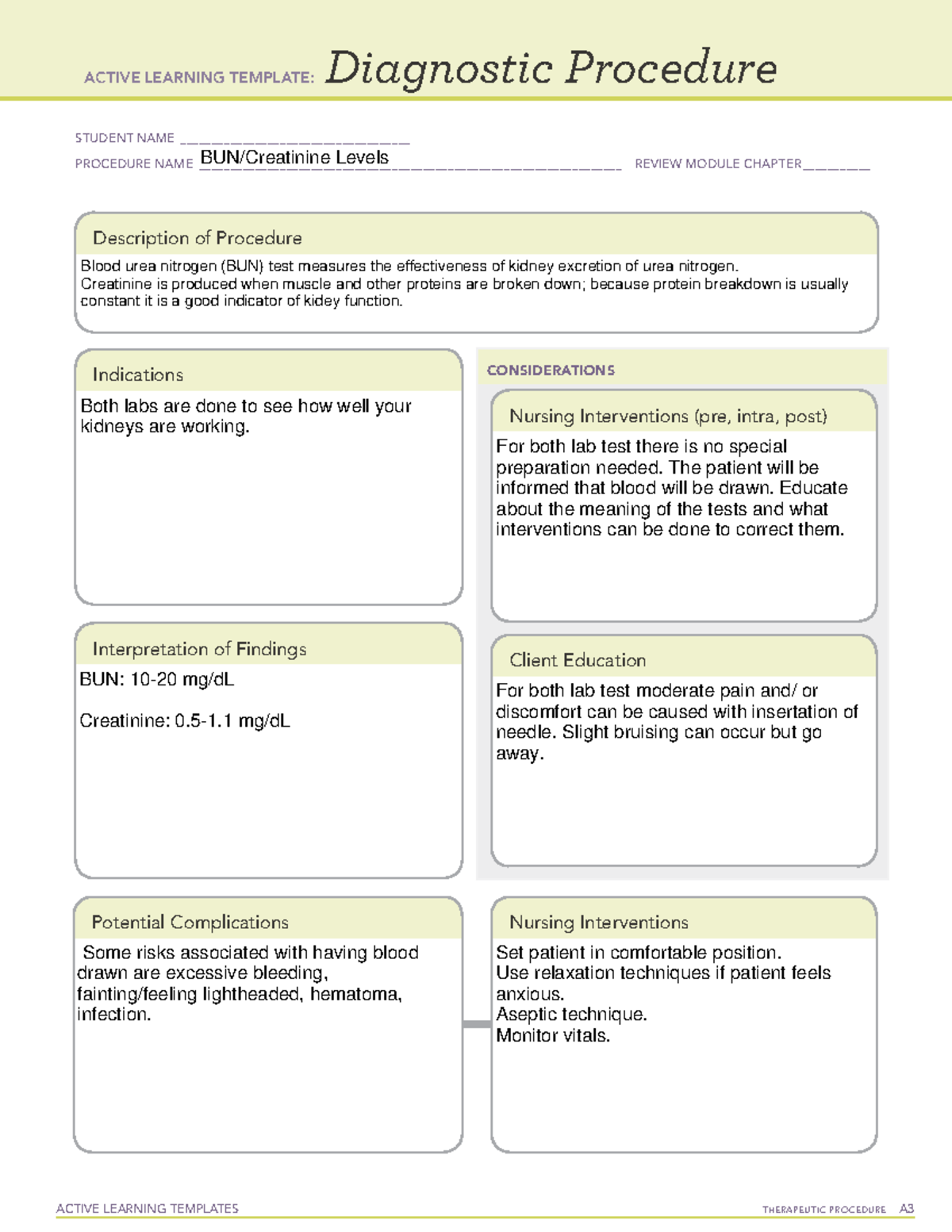
BUN – ATI template – ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES THERAPEUTIC PROCEDURE A – Source www.studocu.com
Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio and Its Impact on Your Dog’s Health
The Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio is a valuable tool that can help monitor your dog’s kidney function and overall health. By understanding this ratio, you can take proactive steps to support your pet’s renal health.
Fun Facts about Canine Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) to Creatinine Ratio
Did you know that the Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio can vary between breeds? Some breeds, such as Pugs and Bulldogs, tend to have higher ratios due to their muscular build.

Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Test: High vs. Low Levels, Normal Range – Source www.webmd.com
How to Optimize the Canine Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) to Creatinine Ratio
Optimizing the Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio involves addressing underlying health conditions that may contribute to kidney dysfunction. Your veterinarian will recommend appropriate treatment plans based on your pet’s specific needs.
What if Your Dog’s Canine Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) to Creatinine Ratio is Abnormal?
An abnormal Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio may require further diagnostic testing, such as an ultrasound or kidney biopsy. Your veterinarian will determine the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment.
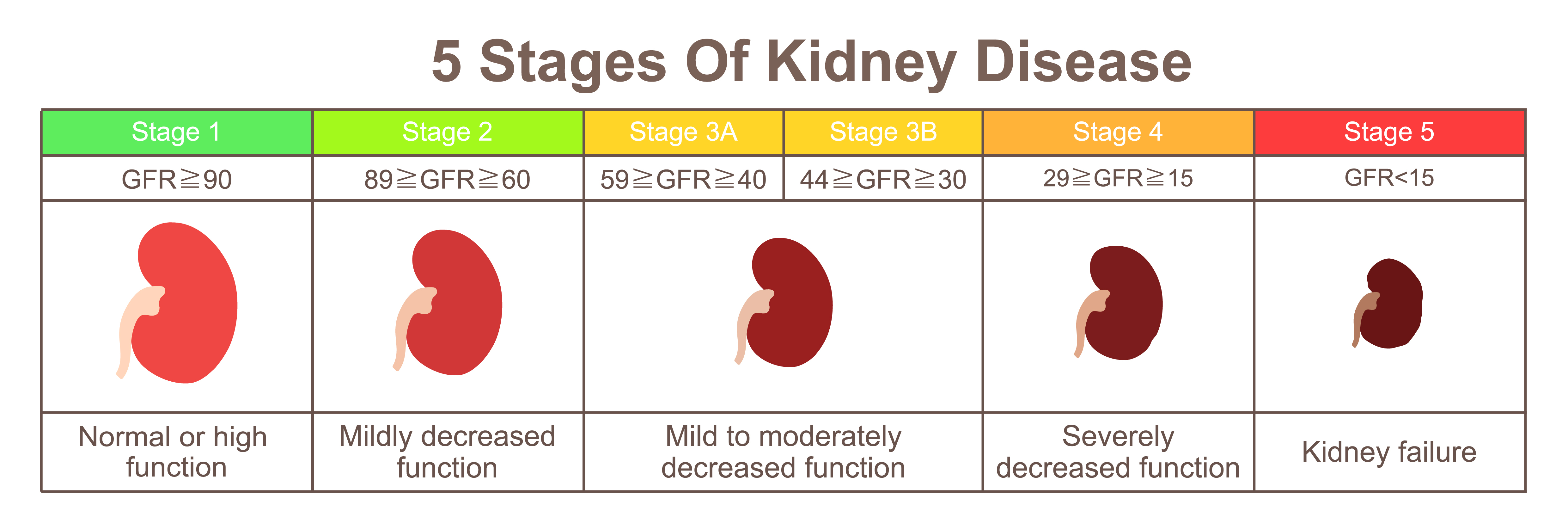
Creatinine Kidney Disease Chart – Source ar.inspiredpencil.com
A Listicle of Canine Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) to Creatinine Ratio Insights
- A ratio above 20:1 may indicate dehydration or protein loss.
- A ratio below 10:1 may suggest kidney disease.
- Other factors that can influence the ratio include breed, age, and diet.
- The Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio is a valuable tool for monitoring canine renal health.
- Regular veterinary check-ups can help detect any potential kidney issues early on.
Question and Answer about Canine Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) to Creatinine Ratio
- Q: What is the normal Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio?
A: 10:1 to 20:1
- Q: What does a high Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio indicate?
A: Possible kidney dysfunction or dehydration
- Q: What does a low Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio suggest?
A: Dehydration or protein-losing nephropathy
- Q: Is a high Canine BUN to Creatinine Ratio always indicative of kidney disease?
A: No, other factors such as diet and hydration can influence the ratio
Conclusion of Canine Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) to Creatinine Ratio: A Novel Diagnostic Marker For Canine Renal Disease
The Canine Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) to Creatinine Ratio is a powerful tool in veterinary medicine for assessing canine renal function. By understanding this ratio, pet owners can work closely with their veterinarians to ensure their furry companions maintain optimal kidney health throughout their lives.